The triple constraint is where managers are faced with making trade-offs between the scope of a project, the time it consumes and it's cost. Within the life cycle of any project, the scope, time and cost with unavoidably change. The three variables are interdependent, and if one variable is changed, the other two will be affected:
- To increase the scope of a project, both the time spent on the project and it's cost will also increase.
- To reduce the time spent on a project, costs will be increased and the scope reduced.
- To reduce the costs affiliated with the project, the time spent on the project will be increased and the scope of the project reduced.
Project management is the making of intelligent decisions in regards to these three variables. Managers often find it difficult to balance these three variables, leading to the development of companies such as The Australian Institute of Project Management (AIPM), who develop programs to assist managers in their project development skills through. Further details on the services AIPM provide can be found here.
Question Two - Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning.
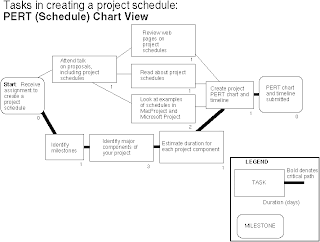 The first main diagram used in project planning is the Program Evaluation and Review (PERT) Chart. This particular diagram is a graphical network model that depicts all the tasks of a project and the relationships that form between it. In particular, it focuses upon the dependencies between such tasks, and the critical paths that need to be followed.
The first main diagram used in project planning is the Program Evaluation and Review (PERT) Chart. This particular diagram is a graphical network model that depicts all the tasks of a project and the relationships that form between it. In particular, it focuses upon the dependencies between such tasks, and the critical paths that need to be followed.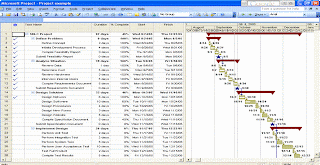
The second main diagram used in project planning is the Gnatt Chart. This form of charting shows the project tasks that must be completed in a simple bar graph against a calender form, allowing time frames in which to complete tasks to be easily identified. Often, database programs such as Microsoft Excel can be used to form the basis of such a chart.
Question Three - Identify the three main areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success.
Manging people - the professional needs of a project must be balanced with the professional and personal needs of a project manager's team of employees. Dealing with people on a day to day basis, and ensuring they understand their role and function, as well as managing and dealing with any conflicts that may arise is the key to ensuring the human component of project management is upheld to the highest standard. The following YouTube video discusses some of the challenges managers face in relation to managing people: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tRzV1dJMErw
Managing communications - likewise, managers must ensure that all communication pertaining to the project at hand are managed and controlled. Communications must be directed at the appropriate persons, ensuring that all vital information regarding the development of the project is directed to right person, ensuring that development will be implemented.
Managing change - managers must be capable of managing changes that may occur throughout the project management process. As mentioned, the three variables of time, scope and cost will inevitable change throughout the life cycle of any project. Thus, it is important for managers to confront these changes and ensure they add to the value of a project, rather than detract from them.
Question Four - Outline two reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects succeed.
Projects fail due to the inability to align the project to the objective of the wider company. An inability to do this would result in a standalone project that may be inconsistent with the overall view of a company, hence making it difficult to gain wider support for such a project within the company. A second reason as to why project fail is due to the inability to move beyond individual and personality conflicts. This is usually the result of poor person management, and can result in a fractured team trying to work upon a singular project. This can result in objectives failing to be fulfilled, and the overall project being inconsistent as a whole.
Projects succeed when sponsorship is gained from the executive level. When executive members of a company support a project, it is likely that the project will be supported throughout the whole organisation. This leads to greater employee input and a greater ability to improve the project with the vast amounts of knowledge provided. Projects are also successful when a good decision making structure has been implemented. This avoids rash and inconsistent decisions being made, and ensures all decisions pertaining to the development of projects are well thought through and considered.